Perspective drawing is the art of creating the illusion of depth and space on a flat surface, transforming your sketches into realistic masterpieces. Whether you’re sketching cityscapes, illustrating interiors, or capturing landscapes, understanding perspective is essential for bringing your drawings to life.
In this guide, we’ll break down the basics of perspective drawing, share 15 quick tips for beginners, and answer frequently asked questions about this fascinating art form.
What Is Perspective Drawing?
Perspective drawing is a technique used to represent three-dimensional objects on a two-dimensional surface. It helps create a sense of depth, proportion, and spatial relationships in your artwork. By understanding the principles of perspective, you can make objects appear closer or farther away, creating a more realistic and engaging composition.
15 Quick Tips for Beginners to Master Perspective Drawing
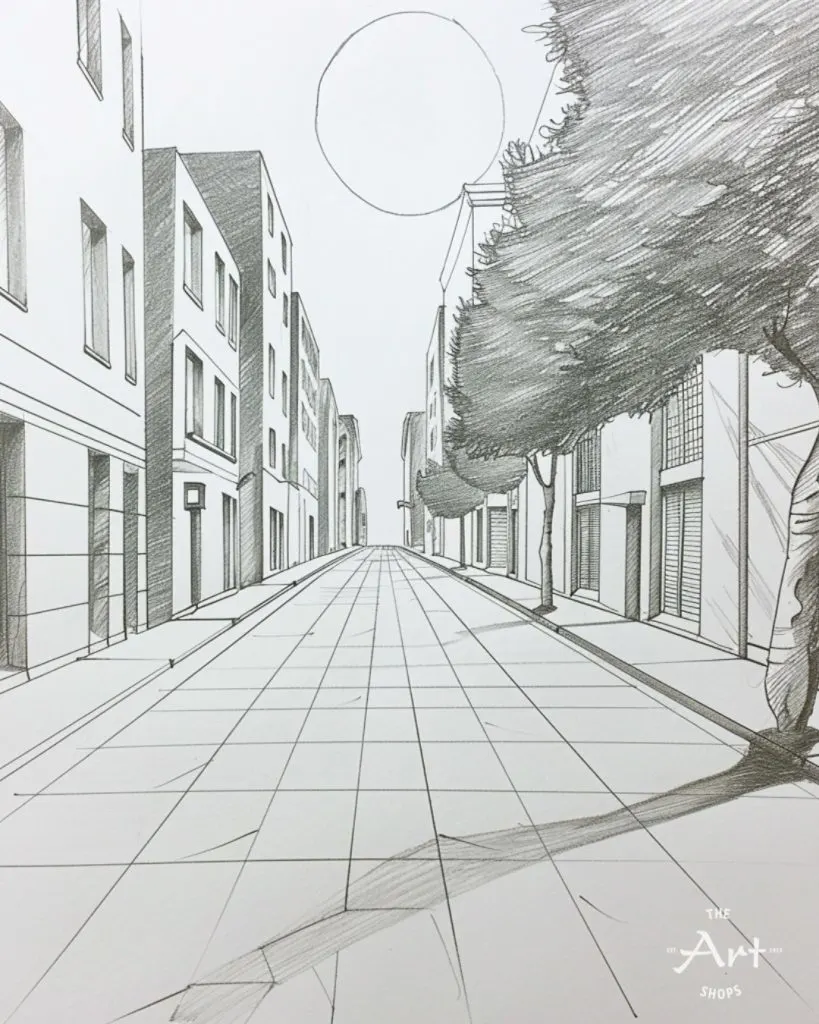

1. Start with a Horizon Line
The horizon line is the foundation of perspective drawing. It represents your eye level and separates the sky from the ground. Establish it early to guide your drawing.
2. Understand Vanishing Points
Vanishing points are where parallel lines converge in the distance. Most drawings use one, two, or three vanishing points, depending on the type of perspective.
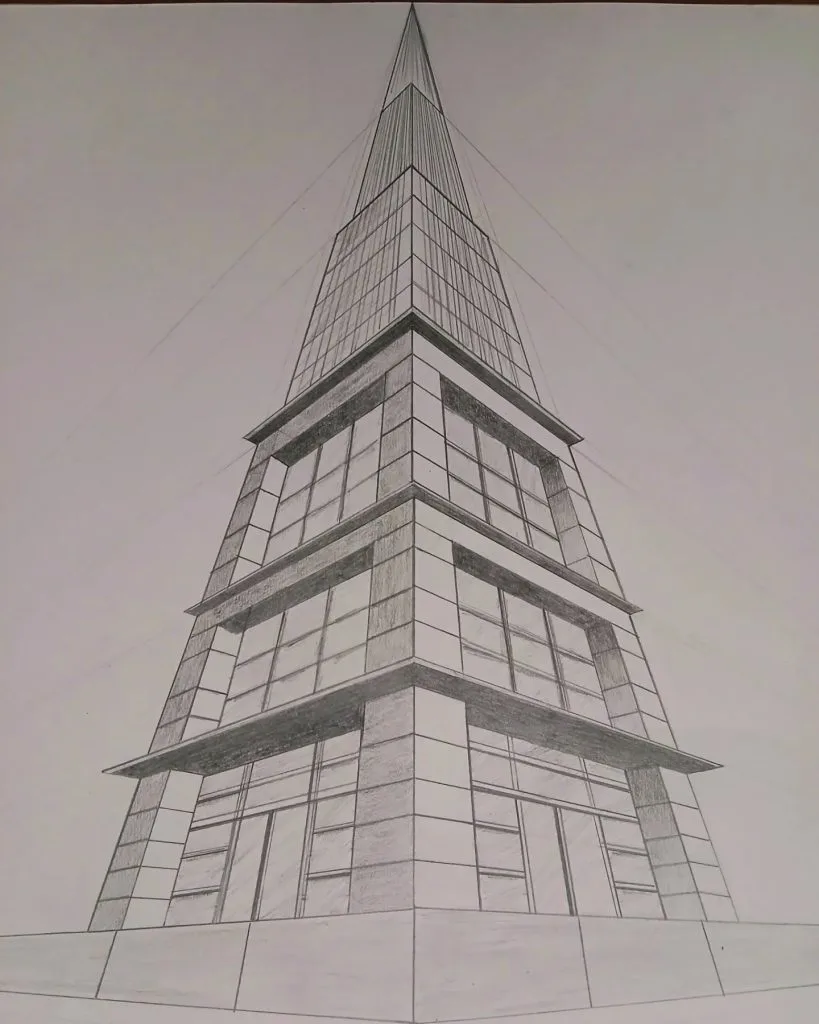

For precise architectural drawings like this, the Pentel GraphGear 1000 offers professional-grade precision and control, making it the perfect tool for technical sketching and shading.
3. Learn the Types of Perspective
- One-point perspective: All lines converge to a single vanishing point.
- Two-point perspective: Lines converge to two vanishing points on the horizon.
- Three-point perspective: Adds a third point, often used for dramatic or towering angles.
4. Use Guidelines
Lightly sketch guidelines to ensure your lines accurately converge at the vanishing points.

5. Practice Simple Shapes
Start with basic shapes like cubes and cylinders. Mastering these forms builds a solid foundation for more complex drawings.
6. Experiment with Overlapping
Overlap objects to create a sense of depth. Objects in front should partially obscure those behind them.
7. Study Real Life
Observe how objects appear smaller as they recede into the distance. Practice sketching scenes from real life to enhance your understanding.

8. Use Reference Images
Work from photos or artwork to practice identifying vanishing points, horizon lines, and perspective principles.
9. Apply Atmospheric Perspective
Objects farther away appear lighter and less detailed due to atmospheric effects. Use shading and texture to achieve this effect.
10. Work on Foreground, Middle Ground, and Background
Divide your composition into layers to create depth. Ensure each layer connects seamlessly to the vanishing points.

11. Master the Four Principles of Perspective
- Size: Objects appear smaller as they move away.
- Overlap: Closer objects overlap those farther away.
- Convergence: Parallel lines appear to meet at a point.
- Detail: Farther objects lose detail and clarity.
12. Avoid Tangents
Ensure objects don’t awkwardly touch the edges of other objects, as this can flatten your drawing.
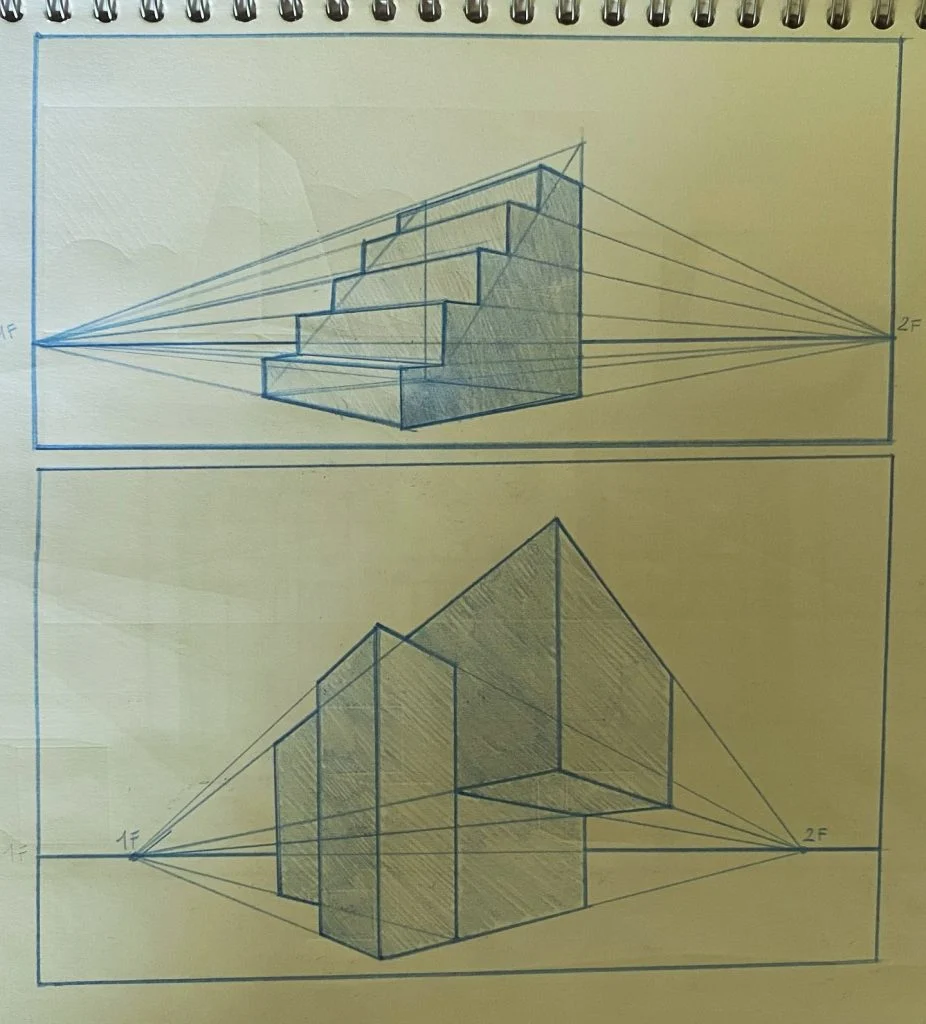
13. Experiment with Different Eye Levels
Vary the height of your horizon line to experiment with different perspectives and angles.
14. Sketch Regularly
Perspective is a skill that improves with consistent practice. Dedicate time to sketch daily.
15. Review and Refine
Constantly critique your work to identify areas for improvement. Use erasers and adjustments to refine your perspective.
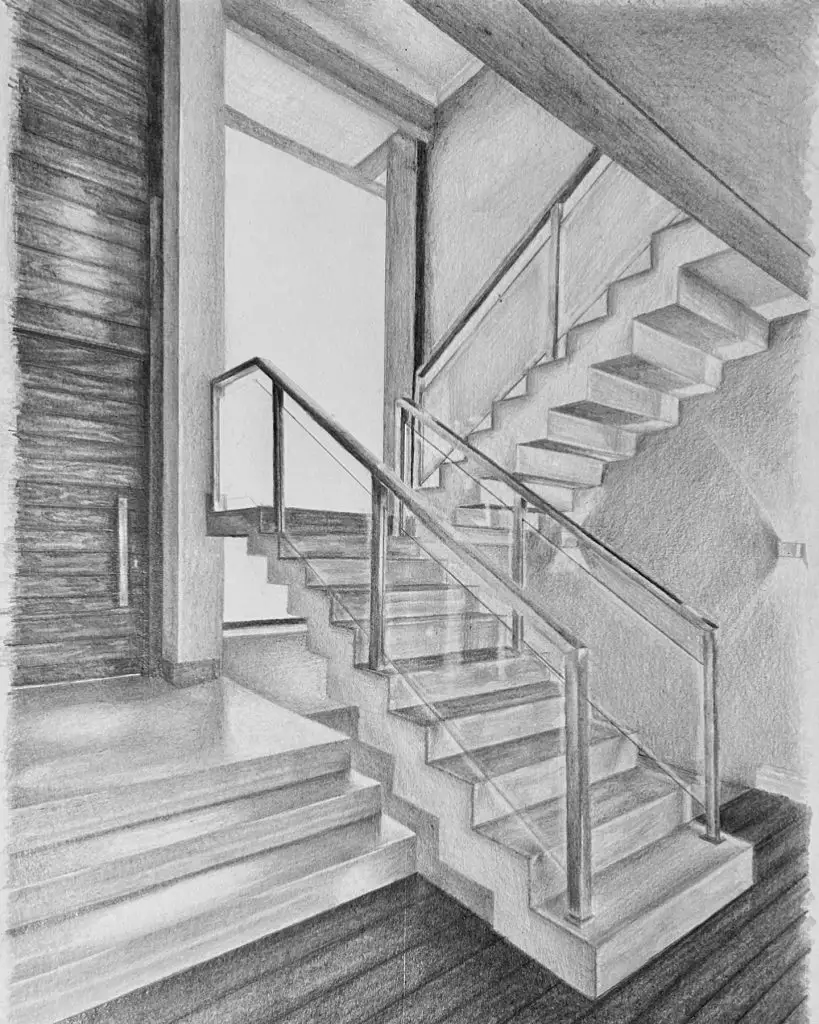

Achieve smooth gradients and precise architectural shading with the Zebra Pen DelGuard Mechanical Pencil— a must-have for professional-level pencil sketching
Perspective Drawing Exercises for Beginners
- Draw a Room: Start with a one-point perspective to sketch a simple room.
- Cityscape Practice: Use two-point perspective to create a city scene with buildings.
- Object Study: Sketch everyday objects like books or boxes using perspective.

Characteristics of Perspective Drawings
- Illusion of Depth: Perspective drawings make flat images appear three-dimensional.
- Vanishing Points: Central to the technique, guiding how lines converge.
- Proportional Accuracy: Objects are drawn in realistic proportions relative to their distance.
- Spatial Relationship: Perspective establishes the placement and scale of objects.
Types of Perspectives
- One-Point Perspective: Great for simple scenes like hallways or roads.
- Two-Point Perspective: Ideal for architectural drawings and landscapes.
- Three-Point Perspective: Adds dynamic angles, often used for tall buildings.
- Zero-Point Perspective: Used for natural landscapes without straight lines.

The 4 Principles of Perspective
- Size: Objects farther away appear smaller.
- Overlap: Closer objects overlap those behind them.
- Convergence: Parallel lines meet at vanishing points.
- Detail and Clarity: Farther objects appear less detailed.

For highly detailed and precise technical sketches like this, the Rotring 600 – Best for Ultimate Precision offers unmatched control and accuracy, making it the go-to choice for professional artists and illustrators.
The 4 Stages of Perspective Taking
- Egocentric: Viewing the scene solely from your perspective.
- Decentered: Understanding how others might view the scene.
- Interactive: Balancing multiple perspectives within a composition.
- Reflective: Critiquing and refining your work for clarity and depth.
People Also Ask
What is perspective drawing?
Perspective drawing is a method to depict three-dimensional objects and spaces on a flat surface, giving the illusion of depth and realism.
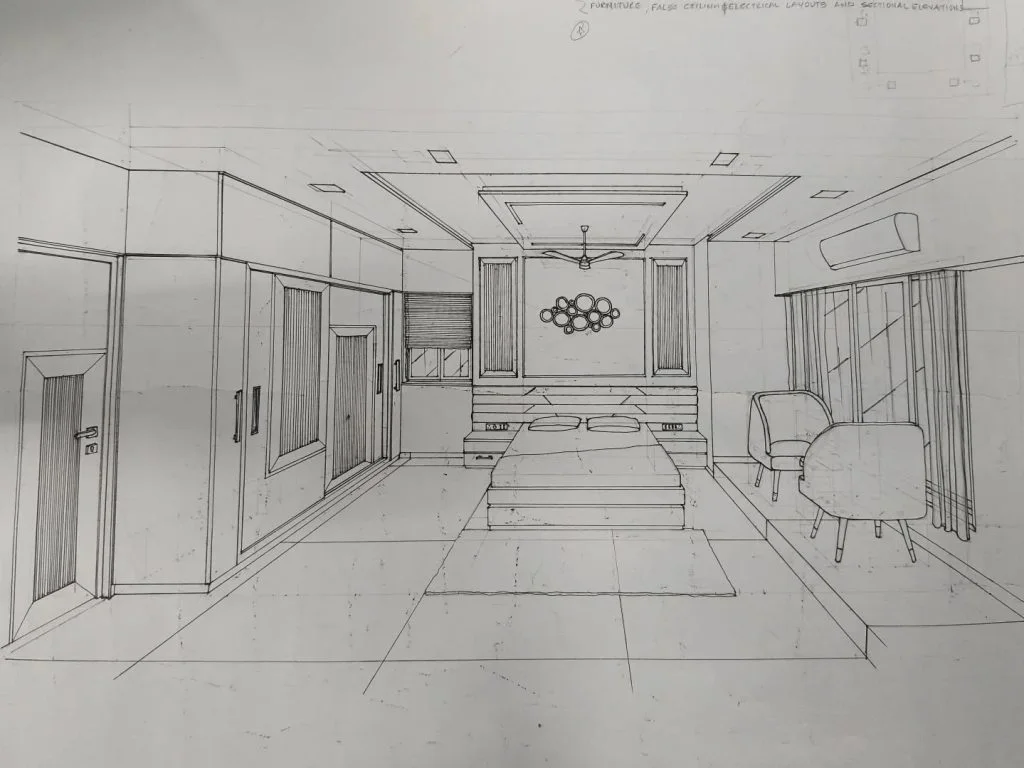
For precise architectural line work and technical drafting like this, the Staedtler Mars Technico Lead Holder (780 C) delivers unmatched precision and control, making it a top choice for designers and illustrators.
What are perspective drawing exercises for beginners?
Try exercises like sketching a room in one-point perspective, creating a cityscape with two-point perspective, or practicing vanishing points with simple shapes.
What are the characteristics of perspective drawings?
Perspective drawings feature depth, vanishing points, accurate proportions, and defined spatial relationships.
What are the types of perspectives?
The main types are one-point, two-point, three-point, and zero-point perspectives.

What are the 4 principles of perspective?
They include size, overlap, convergence, and detail and clarity.
What are the 4 stages of perspective taking?
The stages are egocentric, decentered, interactive, and reflective.
Conclusion
Mastering perspective drawing takes practice and patience, but it’s a rewarding skill that transforms your art. By understanding the principles, experimenting with exercises, and practicing regularly, you can bring depth and realism to your drawings. Use the tips and exercises outlined in this guide to start your perspective drawing journey.
Dive deeper into your artistic journey with these articles from our collection:
- The Art of Drawing Trees: 10 Stunning Sketches You Need to See – A perfect way to practice perspective with natural elements and stunning sketches.
- 35 Easy Drawing Ideas for Beginners: Unlock Your Creative Potential – Simple drawing exercises to refine your skills and build confidence.
- 39 Easy Animals to Draw for Beginners – Great for practicing proportion and depth, essential elements of perspective drawing.
- Creative Therian Mask Ideas to Bring Your Identity to Life – A unique way to experiment with perspective and form.
- Exploring Expressionism Art: The Power of Emotion on Canvas – Learn to add depth and emotion to your perspective drawings.

ATUKUNDA ESTHER
Monday 22nd of September 2025
The work is good
Kendu
Tuesday 14th of October 2025
@ATUKUNDA ESTHER, Hi. Are you an artist in Uganda?